2.3.2 Navigating the Benefits and Challenges of Algae and Insects as Raw Materials
Benefits of utilizing algae and insects as raw materials:
- Environmental sustainability: Algae and insects have a smaller ecological footprint compared to traditional raw materials. They require fewer resources like land, water, and fertilizers, and emit fewer greenhouse gases.
- Nutritional value: Algae and insects are rich in essential nutrients, making them potential sources of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Waste reduction: Both algae and insects can be grown using organic waste streams, such as agricultural residues, food waste, or wastewater, helping to reduce waste and create circular economy systems.
- Versatility: Algae and insects can be used in various industries, including food and feed production, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and bioenergy.
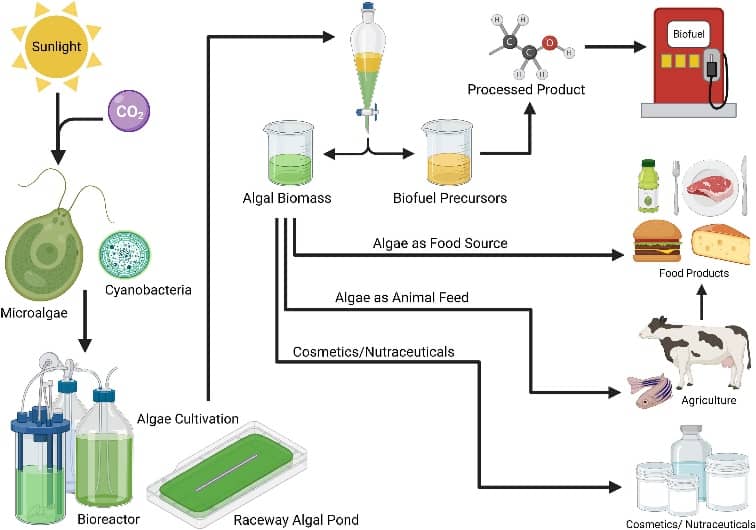
Figure 4- The versatile markets for algae products
Source: Biorender.com
While algae and insects show promising signs as alternative raw materials for food production, there are several challenges associated with their utilization. Some key challenges are the following:
- Cultural acceptance: Algae and insects are not commonly consumed in many Western cultures, and cultural barriers can hinder their acceptance as food sources. Overcoming the stigma and negative perceptions associated with consuming these alternative ingredients can be a challenge.
- Regulatory frameworks: The regulatory frameworks governing the production and consumption of algae and insects as food vary across countries. Establishing clear regulations and standards for safety, labeling, and production practices is essential to ensure consumer confidence and market development.
- Scaling up production: Scaling up the production of algae and insects to meet the demands of a growing population is a significant challenge. Cultivating algae at a large scale requires appropriate infrastructure, access to water, and expertise in algae farming techniques. Similarly, insect farming methods need to be refined and optimized to achieve higher yields and consistent quality.
- Processing and ingredient functionality: Developing efficient and cost-effective processing methods for algae and insects to transform them into food ingredients can be challenging. Extracting desirable compounds and proteins from algae and insects while maintaining their nutritional value and functional properties requires research and innovation.
- Allergenic potential: Allergies to algae and insects can pose challenges for widespread adoption. Some people may have allergic reactions to specific species of algae or insects, making it necessary to identify potential allergens and establish appropriate labeling practices to protect consumer health.
- Taste and sensory aspects: The taste, texture, and overall sensory experience of food products made with algae and insects can be different from traditional foods. Overcoming these sensory challenges and ensuring that products made from alternative ingredients are appealing to consumers is crucial for their acceptance and market success.
- Cost and affordability: Currently, the production costs associated with algae and insect farming are often higher compared to traditional food sources. Economies of scale, technological advancements, and improved production practices are needed to reduce costs and make these alternative ingredients more affordable for consumers.
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between researchers, policymakers, industry stakeholders, and consumers to drive innovation, improve production techniques, and create a supportive regulatory environment for the sustainable utilization of algae and insects as raw materials for food production. However, despite these challenges, ongoing research, innovation, and advocacy are driving the utilization of sustainable raw materials like algae and insects, offering promising solutions for a more sustainable and resilient future. Traditional food substitution with alternative biomass sources is becoming a necessity to design a more sustainable transition to the new food system. Based on current analysis (Zhou Y. et al., 2022), which included comparison of alternative protein sources according to the technology readiness level, nutritional profile and environmental impact, indicated the potential for the substitution of traditional food. Alternative sources of biomass can be used as food substitutes if their environmental and economic benefits are assured. It could be done through the application of agri-food wastes and further development of production technologies.