Introduction to the Module
Competence Description
The food supply chain affects every individual on the
planet. As a result, sustainable development of the food supply chain is imperative. Sustainable development has
been defined as meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet
their needs” (WBCSD, 2000). The food supply chain, also called the food industry or food system, includes
aspects from production of the food, processing, distribution, consumer purchase, consumer use, and end of life. A
sustainable food supply would then mean that food is produced and consumed in a way that supports the well-being of
generations. The current food supply has demonstrated impacts that make it unsustainable. Such impacts include
overreliance on inputs for food production such as high-intensity animal production and production of produce out of
season.
A sustainable food system (SFS) is one that provides food security and nutrition for everyone without
compromising the economic, social, and environmental foundations necessary to produce food security and nutrition
for future generations. This means that:
– It is profitable throughout (economic
sustainability)
– It has broad-based benefits for society (social
sustainability) and
–It has a positive or neutral impact on the natural environment (environmental
sustainability).
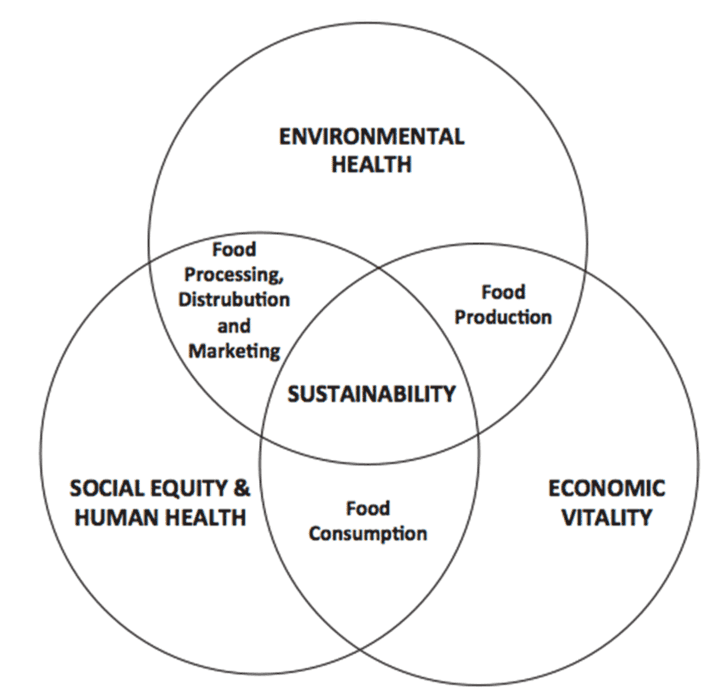
Figure 1 – A sustainable food system (SFS) ensures
environmental, social and economic sustainability.
Source: Adapted from FAO, 2014.
Why is this
Competence important?
In a competitive market, small food businesses that prioritize sustainability can
differentiate themselves from competitors. This unique selling point can attract a niche market segment that aligns
with their values, giving them a competitive advantage. What is more, embracing sustainability requires creative
problem-solving and innovation. Small food businesses that commit to sustainability are more likely to develop new
processes, products, and strategies that can help them adapt to changing market trends and consumer preferences.
Finally, the competence of sustainability is significant for SME’s, because it not only aligns with consumer
preferences, but also provides tangible benefits in terms of operational efficiency, brand image, regulatory
compliance, and long-term viability. By integrating sustainable practices, food SME’s can position themselves for
success in a rapidly changing business landscape.
The learning objectives of this Module are:
- Addressing Food Waste and Loss: Understand the magnitude of food waste and loss in the food
supply chain and explore strategies to reduce waste and improve resource efficiency.
- Understanding Sustainable Raw Materials: Define sustainable raw materials and explain their
significance in promoting environmental conservation, reducing ecological impact, and supporting circular
economy principles.
- Exploring Sustainable Packaging Materials: Explore various sustainable packaging materials and
technologies, including biodegradable plastics, compostable materials, bio-based polymers, recycled content, and
alternative packaging solutions.
Staramaki

Staramaki is a straw
made of wheat. It is produced by a Social Cooperative Enterprise in Kilkis, situated in rural Northern Greece. The
most widely produced local product – wheat – is used to create a viable eco-friendly alternative to single use
plastic straws. The Staramaki products are made from the stalk that is left over when wheat grains are harvested.
The European Commission's announcement in 2020 on the future banning of several single-use plastic products has
highlighted the need for more sustainable alternatives.
Staramaki wheat straw never goes soggy, as it is not
made of pulp, but it comes from the stems of the wheat plant. Moreover, mature forests must be destroyed to harvest
wood for the pulp needed to make paper, which then has to be heavily processed before becoming a final product.
Staramaki, coming from an agricultural output, requires no energy and, as a plant, it seizes CO2 during the stem
elongation phase, plus, it requires no chemicals during manufacturing.
Meanwhile, they create employment
opportunities and promote social cohesion, as well as local and regional development. Rural depopulation is a
serious issue in all of the countries of Western Europe. It is mainly a question of economic opportunities. The
trends in Greece and the rest of Europe reflect a decades-long worldwide population movement from rural to urban
areas. The problem of an ageing population is particularly affecting the Greek countryside. The recent economic
depression, the global pandemic and social crisis have made the need for innovation to address social challenges
even more apparent and acute. It has led to debate and concerns about how to pursue a different approach towards
achieving well-being.
Through social innovation, Staramaki is bringing both growth and social value. It is
demonstrating that there is space for innovative thought in Greece, and that circular economy can become a fertile
field for such innovative actions.
Solmeya

It is a Greek start-up company, which started
in 2019 to provide a sustainable answer to the growing need for proteins, against conventional animal proteins,
which are responsible for 1/3 of methane emissions. How does it do this? It produces proteins from microalgae,
cultivated through hybrid vertical farming, recycling 97% of the water used and using freely available CO2 and
sunlight. Concisely, Solmeyea’s microalgae can be used as a protein alternative in food, nutritional supplements and
animal feed. According to its CEO, Vassilis Stenos, microalgae are considered a superfood, as they contain large
amounts of amino acids and omega-3. As microalgae contain natural oils, they do not need to be mixed with other
added, poor quality oils such as palm oil. It also produces raw materials such as astaxanthin for pharmaceutical,
antiaging, sun protection products with the final recipient being the pharmaceutical industry, cosmetology and
companies producing concentrated plant protection suspensions and insecticides, contributing at the same time to
reversing climate change and improving the quality of natural environment and atmospheric air.
Behind
Solmeyea's "revolutionary" business philosophy there is, however, an even more important practical dimension: with
the combined production of agri-food and food raw materials and cosmetology products and medicines, in addition to
the simultaneous utilization of carbon dioxide, all 9 of the 17 goals for Sustainable Development (Sustainable
Development Goals), as established in 2015 at the United Nations General Assembly in New York, as well as the
financial-sociological environmental criteria of ESG's (Environmental, Social, Governmental) are served. Solmeyea's
goal is only growth, innovation, optimism and brain gain vs brain drain.
Bibliography
Amienyo D., Gujba H., Stichnothe H. & Azapagic A., «Life cycle environmental impacts of
carbonated soft drinks», The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, vol. 18, 77–92, 2013.
Buzby J.C., Wells H.F., Aulakh J., Food loss—Questions about the amount and causes still remain, 2014.
Caldeira C., Valeria De Laurentiis , Corrado S., Freija van Holsteijn , Sala S., «Quantification of food waste per
product group along the food supply chain in the European Union: a mass flow analysis», Resources, Conservation
and Recycling, vol. 149, Oct. 2019, pg. 479-488.
Carmona-Cabello M., Isabel L. Garcia, David
Leiva-Candia, M. Pilar Dorado, «Valorization of food waste based on its composition through the concept of
biorefinery», Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, vol. 14, December 2018, Pages 67-79.
Dahiya, S., Kumar, A.N., Shanthi Sravan, J., Chatterjee, S., Sarkar, O., Mohan, S.V., «Food waste biorefinery:
sustainable strategy for circular bioeconomy», Bioresource Technology, vol. 248, 2–12.
Dou Z., James
D. Ferguson, David T. Galligan, Alan M. Kelly, Steven M. Finn, Robert Giegengack, «Assessing U.S. food wastage and
opportunities for reduction», Global Food Security, vol. 8, March 2016, 19-26.
EC (European
Commission), Closing the Loop - an EU action plan for the circular economy, 2015, Brussels.
FAO (Food
and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations), The State of Food and Agriculture, Rome, 2015.
FUSIONS (Food Use for Social Innovation by Optimising waste prevention Strategies), Definitional Framework for
Food Waste, Vittuari M., 2016, University of Bologna, Italy.
García-Arca, J., & Prado-Prado, J.
C., «Packaging design model from a supply chain approach», Supply Chain Management: An International
Journal, 13(5), 375-380.
Joint Research Centre, European Union Reference Laboratory for Food Contact
Materials, 2014.
Jönson, G., Packaging Technology for the Logistician, 2nd ed., Lund University,
2000.
Molina-Besch K., Prioritization guidelines for green food packaging development, Lund
University, 2016.
Obi F. O., Ugwuishiwu B. O., Nwakaire J. N., «AGRICULTURAL WASTE CONCEPT, GENERATION,
UTILIZATION AND MANAGEMENT», Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 35, No. 4, Oct. 2016, pp. 957 –
964.
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), Paris, 1997.
Pawelczyk A., EU
policy and legislation on recycling of organic wastes to agriculture, 2005, Warsaw, Poland.
World
Business Council on Sustainable Development (WBCSD), Eco-Efficiency: Creating More Value with Less Impact,
2000, Conches-Geneva, Switzerland.
Waste & Resources Action Programme (WRAP), United Kingdom, 2007.
Zhou Y., Liu L., Li M., Hu C., « Algal biomass valorisation to high-value chemicals and bioproducts: Recent advances,
opportunities and challenges», Bioresource Technology, vol. 344, part B, January 2022.



