Introduction
This is a turning point in our history: as the world population continues to increase, we need to keep supplying safe, affordable, high-quality, and nutritious food while preventing severe rises in global temperatures and biodiversity loss. Although there has been some progress, we still need to work harder to enhance the methods by which we produce, develop, and use food and drink items.
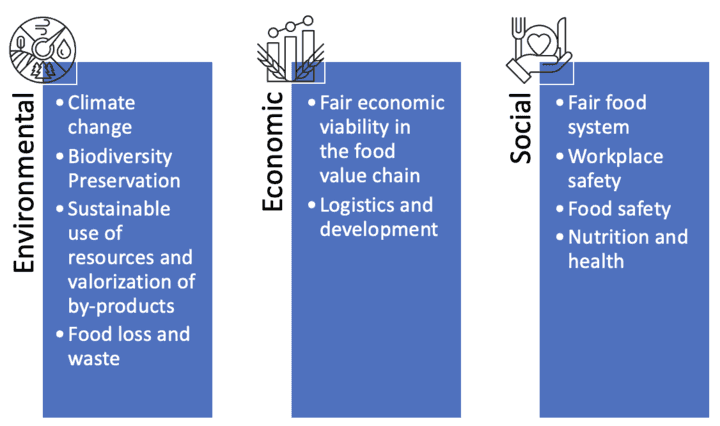
More sustainable food systems are a general challenge at a global scale, targeting high-level objectives for the transition, with the participation of all actors of the supply chain, together with Institutions and both private and public sectors. The effort to mitigate the impacts on the ecosystem would be insufficient without taking into account the economic and social dimensions of sustainability, which are included in the notion of sustainability, in addition to the environmental one. The challenge at hand involves reconstructing the fundamental beliefs that underpin development and progress from a worldwide viewpoint that encompasses the environment, society, and economy.
Which are the features of each pillar of sustainability?